8 September 2025
5 minutes read
What is the Difference Between MS and MEng in USA (Master of Engineering vs Master of Science)?

Key Takeaways
- Difference between MS and MEng in USA lies in their focus, with MS being research-intensive and MEng emphasizing practical industry applications.
- It affects career prospects, as MS leads to research and academic roles, while MEng prepares students for engineering careers.
- It also impacts duration, with MS typically taking two years and including a thesis, while MEng is a one-year professional degree.
It can be difficult for students to decide between a Master of Science (MS) and a Master of Engineering (MEng) degree in the USA. Both are great career prospects in engineering, but they have very different structures, emphases, and conclusions. If you are a foreign student wanting to study an engineering postgraduate degree, recognizing these differences is important. The following article compares MS and MEng in an extensive manner so that you may decide which course suits your future career.
What is a Master of Science Degree (MS) in Engineering?
Master of Science is a research-oriented degree program intended for students who want advanced theoretical knowledge and research in academics. It is more normally abbreviated as MS or MSc and is widely available in mechanical, civil, chemical, computer, and electrical engineering.
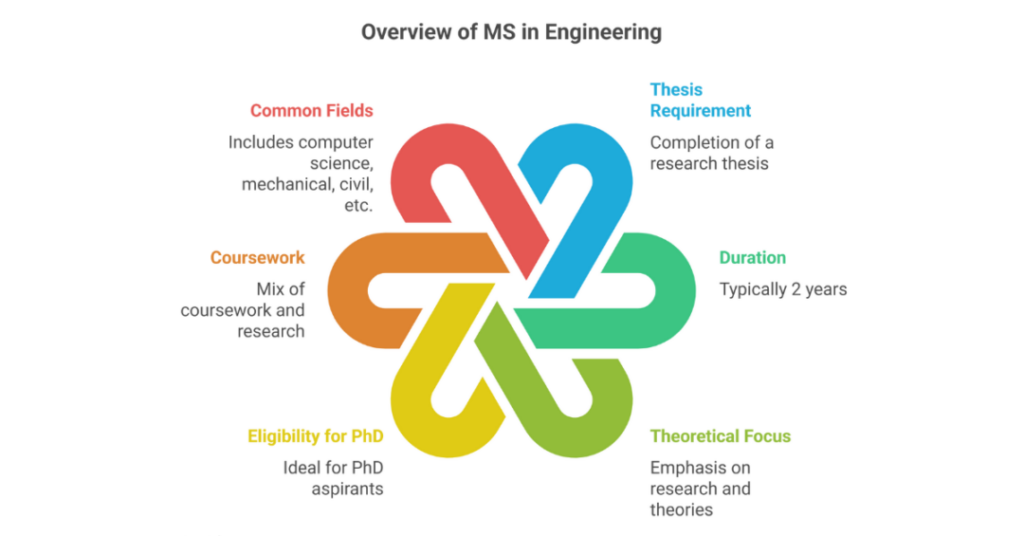
Key Features of Master of Science in Engineering:
- Thesis Requirement: Students are required to complete a research thesis, which contributes to the field’s knowledge base.
- Duration: Typically 2 years (can vary based on research progress).
- Theoretical Focus: Emphasizes research, applied mathematics for engineering, and fundamental engineering theories.
- Eligibility for PhD: Completing an MS is ideal for students who want to pursue a PhD.
- Coursework: A mix of coursework and research-based learning.
- Common Fields: Computer science, mechanical, civil, environmental, and electrical engineering.
What is a Master of Engineering (MEng)?
A Master of Engineering degree (MEng) is a professional degree with a focus on the application of engineering principles in practice. In contrast to an MS, an MEng program does not usually have a thesis requirement, so it is a shorter degree, usually taken in one year.
Key Features of MEng:
- No Thesis Requirement: Instead of a thesis, students work oncapstone projects or case studies.
- Duration: Usually one year to complete.
- Practical Focus: More industry-oriented, preparing students for engineering roles in the employment market.
- Not Research-Oriented: Unlike the MS degree, this program does not prepare students for a PhD.
- Coursework-Based: Heavily focused on engineering career skills.
- Common Fields: Mechanical, civil, chemical, computer, and electrical engineering.
Comparison Between MS and MEng Degrees
Deciding between an MS and a MEng course of study can be hard for students seeking to develop their careers in the engineering profession. Both courses have specialized skills and knowledge but vary in composition, concentration, and career prospects. When choosing a master ‘s degree, one should consider how each program relates to one’s undergraduate studies and career goals.
The potential salary of graduates also depends on whether they pursue an MS or MEng. It is essential to learn the difference between Master of Science vs Master in Engineering to take an informed decision. We present in the following an extensive comparison between MEng and MS so that the student can determine which degree would be most appropriate according to their interests.
Key Differences: MEng vs MS:
| Feature | Master of Science (MS) | Master of Engineering (MEng) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Theory-oriented, Research-Oriented | Industry-Oriented, Practical |
| Thesis Requirement | Yes, research-based thesis | No, capstone project or coursework |
| Duration | Typically 2 years | 1 to 1.5 years |
| PhD Pathway | Ideal for PhD aspirants | Not a common pathway to PhD |
| Employment Market | Suitable for academic and research roles | Best for direct entry into engineering jobs |
| Common Fields | Mechanical, Electrical, Civil, Chemical, Computer Science Engineering | Mechanical, Civil, Electrical, Environmental, Industrial Engineering |
| Salaries | Varies based on research background | Often higher initially due to industry alignment |
Which Degree is Right for You?
Selecting between an MS and an MEng is based on your career aspirations, salary requirements, and whether you want a science vs master of engineering programs style. If you’re looking at ms abroad, knowing whether one degree is more suitable for your goals is crucial. Although an MS is usually regarded as a non-professional degree with a research orientation, a Master of Science and Master of Engineering both offer good career prospects.
A masters degree could focus on learning, while an MEng or MSc degree is application-oriented. In order to make an informed decision, comparing ms vs MEng in coursework, career opportunities, and industry demand is essential.
Choose an MS if:
- You are interested in academic research.
- You plan to pursue a PhD.
- You enjoy working on theoretical concepts and science programs.
- You want to contribute to engineering and masters of science innovations.
Choose an MEng if:
- You want a shorter, industry-focused degree.
- You are looking for engineering career opportunities in the employment market.
- You prefer practical application over research.
- You want to complete your graduate degree quickly and start working.
Admission Requirements for MS and MEng
Most universities in the USA require students to submit the following:

- Bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field.
- Standardized test scores: GRE, IELTS, TOEFL, SAT.
- Letter of recommendation from professors or employers.
- Statement of Purpose (SOP).
- Resume and work experience (if applicable).
Job Market and Salary Expectations
Salaries vary between MS and MEng graduates, but both degrees offer strong earning potential.
| Degree | Average Starting Salary (USD) | Common Job Roles |
| MS | $80,000 – $110,000 | Research Engineer, Data Scientist, Software Developer |
| MEng | $85,000 – $120,000 | Project Engineer, Manufacturing Engineer, Design Engineer |
Fun Fact:
- Engineering professionals with a master’s degree earn 20-30% more than those with just a bachelor’s degree.
- The engineering field is expected to grow by 7% over the next decade, making both degrees exceptional choices for international students.
Master of Engineering vs Master of Science: Which is Better?
It varies based on what you are trying to achieve. If your concern is academic research, an MS program is a better option. But if you are looking to join the workforce immediately, an MEng is a professional master’s that allows you to start working right away.
Top 10 Universities for MS and MEng in USA
Choosing the right university for MS or MEng in the USA can play a key role in determining the career path of a student. Tuition costs, salary rates, QS World University Rankings 2025, and the courses available should be taken into consideration before choosing.
Here is a comprehensive comparison of the top 10 universities for MS and MEng in the USA.
| University | Tuition Fees (Annual) | Average Salary (Post-Graduation) | QS Ranking 2025 | MS Programs Offered | MEng Programs Offered | Exam Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIT | $57,590 | $120,000 | 1 | Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Computer Science | Civil Engineering, Aerospace Engineering | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Stanford University | $56,169 | $115,000 | 2 | Computer Engineering, Environmental Engineering, Chemical Engineering | Structural Engineering, Systems Engineering | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Harvard University | $54,880 | $110,000 | 3 | Biomedical Engineering, Applied Mathematics for Engineering | Energy Engineering, Robotics | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| UC Berkeley | $48,435 | $105,000 | 4 | Software Engineering, Data Science | Industrial Engineering, Materials Science | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Caltech | $54,600 | $108,000 | 5 | Electrical Engineering, Applied Physics | Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Carnegie Mellon University | $50,100 | $102,000 | 6 | Artificial Intelligence, Robotics | Manufacturing Engineering, Systems Engineering | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| University of Michigan | $51,200 | $98,000 | 7 | Aerospace Engineering, Civil Engineering | Automotive Engineering, Energy Systems | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Columbia University | $55,056 | $99,500 | 8 | Computer Science, Data Analytics | Environmental Engineering, Transportation Engineering | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| Princeton University | $52,800 | $97,000 | 9 | Electrical and Computer Engineering, Quantum Engineering | Bioengineering, Smart Infrastructure | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
| University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign | $46,790 | $95,000 | 10 | Software Engineering, Bioinformatics | Agricultural Engineering, Nanotechnology | GRE, TOEFL/IELTS |
Conclusion
Both MEng and MS degrees are wonderful options for foreign students considering studying in the USA. The only difference between an MS and a MEng is their direction and design—one is industry-oriented (MEng), while the other is research-oriented (MS). Knowing your personal and professional goals and your undergraduate degree qualification are vital in making the best choice.
If you are still in doubt, consider seeking advice from academic advisors, comparing the programs offered by QS World University Rankings, and evaluating the quality of education at different universities. Pursuing a Master ‘s in both degrees lead to high-paying jobs in engineering, so make an informed decision!
Do you want to study in USA? Schedule a call with the experts at Ambitio now and give your dreams a head start!
FAQs
What is the difference between MS and MEng in USA?
MS is research-focused with a thesis option, while MEng is a professional degree emphasizing coursework and practical application.
Which is better: MS or MEng in USA?
It depends on career goals—MS suits research and academic careers, while MEng is ideal for industry-focused roles.
Does the difference between MS and MEng in USA affect salary?
Yes, MS graduates may earn more in research and academia, while MEng graduates often secure high-paying industry positions.
How does the difference between MS and MEng in USA impact job opportunities?
MS graduates often work in R&D or academia, while MEng graduates enter applied engineering and managerial roles.
Is MEng in USA suitable for international students?
Yes, but MEng is usually shorter, which may impact visa extensions compared to an MS degree.
Do all universities in the USA offer both MS and MEng programs?
Not all universities offer both; some focus on either research-based MS programs or industry-oriented MEng degrees.
Can I switch from MEng to MS in the USA?
Some universities allow switching, but it depends on program policies and additional coursework requirements.

You can study at top universities worldwide!
Get expert tips and tricks to get into top universities with a free expert session.
Book Your Free 30-Minute Session Now! Book a call now




























